Everything You Need to Know About Business Credit Scores … And How to Get the Business Credit You Need.
Some Straight Talk About How to Maintain a Strong Business Credit Score.
Note: We have partnered with Nav to provide business credit monitoring and may make a commission when you use our link. This has no impact on the price you pay.

What is Business Credit Score?
Business credit is credit under a company’s EIN. It has no association with the owner’s Social Security number. It is separate from personal credit, and therefore a business credit score can differ drastically from your personal credit score.
This is credit in the business’s name and it is based on the business’s ability to pay, not the business owner’s. When done right, it is possible to get some business funding based on a business credit score without a personal guarantee. Also, you, the company owner, aren’t personally liable for the credit the business gets.
However, your consumer credit score can still affect your ability to get funding. In some cases, such as with FICO SBSS, personal credit is even used in the business credit score calculation. What other information is used to calculate your business credit score? Is it really possible to get funding without a personal guarantee? It depends on the provider, and the credit reporting agency (CRA) they choose to use.
To build business credit, and get the best business credit cards (even just one business credit card), you will need to know about scores.
D&B Business Credit Scores
D&B constantly gathers data and works to improve its analyses to ensure the greatest degree of accuracy possible. To ensure as accurate a report as possible, it quite literally pays to provide D & B with your company's current financial statements.
PAYDEX
The DB PAYDEX Score is Dun & Bradstreet's main score. It tells the financing provider how well your business has paid the bills over the past year. D & B bases this score on trade experiences documented by vendors. It ranges from 1 to 100. The higher the score, the lower the perceived risk. In business credit terms, it is the most similar to the personal FICO score. This is why it is the most popular business credit option among lenders.
If a small business owner pays attention to nothing else, they should make sure they understand PAYDEX. It can be the difference between getting a credit card and no credit card. And bad credit of any sort can affect the interest rate you’ll pay.
In order to get a PAYDEX score, you need a D-U-N-S Number. This 9-digit number is a unique identifying number that works to establish a business credit file with D & B. A D-U-N-S (Data Universal Number System) works to keep accurate and timely data on over 250 million businesses around the globe. You want your business to be one of them.
From an identification standpoint, it makes a lot of sense. With the use of this identifier, errors can be kept to a minimum. As a result, Dun & Bradstreet will never confuse your business with someone else’s.
Dun & Bradstreet requires that you register your company for free on their site to get a number. There are a few other ways to get a D-U-N-S if your business belongs to a special class. These include if it is a US government contractor or grantee, your company is Canadian, or you are working as an Apple developer.
Registration is fast and simple. Once you have said yes to their Terms and Conditions, you are taken straight to a dashboard where you either ask for a D-U-N-S number or you look up to see if your business is already listed. If it is already on the big list, then you click on your company’s name to make any needed changes.
How it’s calculated
6 Different Types of D&B Scores
There isn't just one Dun and Bradstreet business credit report. They offer six different types of reports. Dun and Bradstreet credit reports are used frequently by lenders to help determine the fundability of a business. That is, whether a business can make money and whether it can pay back a loan or credit.
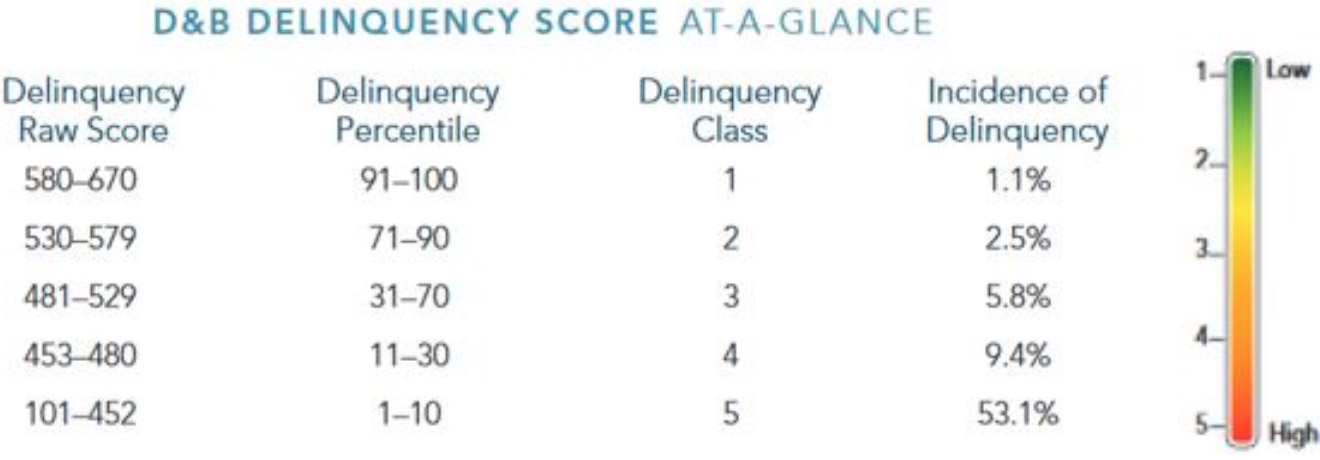
This score measures the chance the company will not pay, will be late paying, or will fall into bankruptcy. The raw score is measured on a scale of 101-670 where 670 is the best possible. Companies are put into classes numbered from 1 to 5. A business in class one 1 is predicted to have the least delinquency risk with a raw score of 580 to 670. A class 2, or a raw score of 530-579, is considered to be good. If a company is in class 5, they have over a 53% instance of delinquency with a raw score of 101-452.
This chart from D&B lays it out nicely.
Per D&B, “The D&B Failure Score (formerly the Financial Stress Score) predicts the likelihood that a business will, in the next 12 months, seek legal relief from its creditors or cease business operations without paying all its creditors in full.” Similar to the Delinquency predictor score, it groups companies into classes. The chart below from D&B directly explains it well.

As you can see, the best class is class 1, with a raw failure score of 1570-1875. Again, being a class 2 company, with a raw failure score of 1510-1569, is considered good. You do not want to be a class 5 company.
This is a rating that ranks the odds of a company surviving 12 months. The lowest score is 9 and the highest is 1. A score of 5 is good.
The credit limit recommendation shows what D&B has calculated to be a business’s borrowing capacity. It is a dollar amount recommendation for how much debt a company can handle. Creditors often use it to determine how much credit to extend.
This is an estimation of overall business risk on a scale of 4 to 1, with a score of 2 being considered good. The smaller the number, the better. It is a combination of letters and numbers. At the high end, a 5A rating indicates a company with a net worth of more than $50 million, while an HH rating at the low end represents a company with a net worth less than $5,000.
Here is how the composite part of this part of your D&B credit history works. First, it represents a company’s overall creditworthiness. It’s based on payment history, years in business, public records, number of employees and financial information. The scale ranges from 1 to 4.
It looks like this:
A score of one is the most creditworthy. If your company has not submitted financial information to Dun & Bradstreet, the highest they can get is a 2. This number is combined with the letter/ number combination above that indicates net worth. This gives an overall view of a company’s size and creditworthiness.
So, if a company has a rating of 4A3, the 4A part means the company’s net worth is $10,000,000 to $49,999,999, and the 3 indicates that the company is a “fair” credit risk.
If there isn’t enough data on a business to assign a regular Dun & Bradstreet credit rating, an alternative score known as a credit approval score is assigned. That one is based on the number of employees. Dun & Bradstreet will use any data they have available to calculate this alternative rating. A company can control this to a point by ensuring D&B has all of the information they need
Commercial Credit Score
Along with the PAYDEX score and other reports above, Dun & Bradstreet also issues a commercial credit score in three parts. Each part predicts how likely the business is to default on bills or become delinquent. This kind of predictive scoring helps a credit determine what might happen with a company in the future based on current data.
Commercial credit score
Commercial Credit Percentile and Class
How Does D&B Get Their Information?
They use what they call the Dun & Bradstreet Data Cloud. According to them, it is “the world’s most comprehensive business data and analytical insights to power today’s most crucial business needs.” But, where does the information in the data cloud come from? It’s pulled from a number of sources including public records, payment histories reported by creditors, information from the company itself, and other data agencies such as LexisNexis and the Small Business Finance Exchange among others.
Equifax Business Credit Report
Equifax is another of the main business credit bureaus. It shows 5 distinct business determinations on its business credit reports.
index
trend
risk score for
suppliers
score
Equifax Payment Index
Like PAYDEX, this score from Equifax is a measurement on a scale of 1 to 100. It shows how many of your small business’s payments were made on time. It uses data from both creditors and trade credit providers. But it’s not meant to anticipate future behavior. That is what the other two scores are for.
Equifax Credit Risk Score for Financial Services
This score for financial services predicts the likelihood of severe delinquency or charge-off over the next 12 months. It is measured on a scale of 101-992. The lower the score, the higher the risk.
Small Business Credit
Risk Score for Suppliers
This score predicts severe delinquency or change-offs on supplier account, or bankruptcy, within 12 months. It ranges from 101 to 816. The higher the number, the better.
Equifax Business Failure Score
This score from Equifax takes a look at the risk of your business shutting down. It runs from 1,000 to 1,600 and bases its scoring on a few different factors. The total balance to total current credit limit is a big one. So is the average utilization in the past three months. Equifax also takes note of the amount of time since the opening of the oldest financial account. So is your small business’s worst payment status on all trades in the last 24 months. After that it considers, proof of any non-financial transactions (like merchant invoices) which are late or are on a charge off for two or more billing cycles.
For the credit risk and the business failure scores, a rating of 0 means bankruptcy.
Equifax Payment Trend
The Payment Trend shows a 12-month payment trend in comparison to the industry norm. It measures the average days beyond terms by the date reported for non-financial accounts only.
This trended data is used to identify businesses more likely to default or declare bankruptcy, and to monitor on-going account activities. It is also used to refine and monitor underwriting and modeling strategies, predict propensity to pay, and identify abnormal spending patterns to reduce fraud and delinquency.
Experian Business Credit Report
Another of the largest business credit reporting agencies, Experian gathers the same general data from many of the same sources as Dun & Bradstreet. Their reports are similar. There are a few key differences in sources, calculation, and presentation.
Intelliscore Plus
This is Experian’s most important score. It shows a statistics-based credit risk. It is a highly predictive score meant to help users make well-informed credit decisions.
The Intelliscore business credit scores range from 1 to 100, with a higher score indicating a lower risk class.
How Does Experian Business Credit Calculate
the Intelliscore Plus Score?
One of the things Intelliscore is most known for is the identification of key factors. These can show how likely a business is to pay its debt. Over 800 commercial and owner variables go into calculating this score. Many of them are from the list of general information all credit agencies look at. But some are more detailed or even unique to Experian. Here is how they are broken down.
Payment History
Frequency
Frequency also incorporates information about your payment patterns. Were you regularly slow or late with payment? Did you decrease the number of late payments over time? That affects your score.
Monetary
Of course, if you are a new company owner, a lot of this information will not exist yet. Intelliscore handles this by using a blended model to identify your score. This means your personal credit score becomes part of determining your business's credit score.
Payment History
This is a one-page report that provides a summary of the business and its owner. Experian has found that a combined business-owner credit scoring model works better than a business or consumer only model. Blended scores have been found to outperform consumer or business credit scores alone by 10 – 20%.
This means that, with Experian, good business credit, in part, comes from a good credit score on the consumer side.
Experian Financial Stability Risk Score (FSR)
FSR predicts the potential of a business going bankrupt or not paying its debts. The score identifies the highest risk businesses by using payment and public records. They use many factors to make their predictions, including high use of credit lines, severely late payments, tax liens, judgments, collection accounts, high risk industries, and length of time in business.
How Long Does Data Stay on Your Experian Report?
According to Experian:
"Bankruptcies remain on file for 10 years after the filing date. Judgments for 7 years after the filing date. Tax liens for 7 years after the filing date. Collections remain on file for 6 years and 9 months after the last report date. UCC filings for 5 years after the last filing date. Bank, government and leasing data for 36 months. Trade data for 36 months after the last report date. Credit inquiries for 9 months."
Check out a sample Experian business credit report.
FICO SBSS
A bit different from your standard business credit reporting agency, the FICO SBSS is the business version of your personal FICO credit score. It is becoming more common for lenders to use this score, rather than the Experian business credit score or even the D&B PAYDEX. It stands for FICO Liquid Credit Small Business Scoring Service.
The Small Business Administration depends on this score when making lending decisions. You will need a good business credit score to get an SBA loan.
Unlike your personal FICO, the SBSS reports on a scale of 0 to 300. The higher the score, the better. But most lenders demand a score of at least 160.
How is the FICO SBSS Scored?
Business owners cannot access their FICO SBSS on their own. There is a proprietary formula for score calculations. FICO does not make that information public. You apply for a business loan blind about what your FICO SBSS credit score may be. This is unlike with the other credit agencies, where you can get a copy of your credit report and know where you stand.
The FICO SBSS Scoring Process
First, FICO gets the request from the lender. FICO then searches business credit information from business CRAs. These include D&B, Experian, and Equifax. If they cannot pull enough scoring information from one, they move onto the next. If there is not enough data from any of them, then it uses personal credit and business financials only.
With the lender's weighting preferences, personal credit, business credit, and business financial data, they calculate the FICO SBSS. This information is specific to that lender.
Payment History
This is a one-page report that provides a summary of the business and its owner. Experian has found that a combined business-owner credit scoring model works better than a business or consumer only model. Blended scores have been found to outperform consumer or business credit scores alone by 10 – 20%.
Experian Financial Stability Risk Score (FSR)
FSR predicts the potential of a business going bankrupt or not paying its debts. The score identifies the highest risk businesses by using payment and public records. They use many factors to make their predictions, including high use of credit lines, severely late payments, tax liens, judgments, collection accounts, high risk industries, and length of time in business.
How Long Does Data Stay on Your Experian Report?
According to Experian:
"Bankruptcies remain on file for 10 years after the filing date. Judgments for 7 years after the filing date. Tax liens for 7 years after the filing date. Collections remain on file for 6 years and 9 months after the last report date. UCC filings for 5 years after the last filing date. Bank, government and leasing data for 36 months. Trade data for 36 months after the last report date. Credit inquiries for 9 months."
Check out a sample Experian business credit report.
Personal Credit Scores
Equifax, FICO, and Experian report on personal credit as well. Dun & Bradstreet does not; the big personal CRA (aside from Experian, Equifax, and FICO) is TransUnion.
The FICO is probably the most commonly used personal credit report, but they all count. They can each vary, but usually only slightly.
Business Credit Scores
Personal Credit Scores
The biggest difference is that a business credit score is based on the business’s ability to pay, not the owner’s. However, business credit differs from personal credit in a number of other ways as well. Various factors affect your business credit score in ways vastly different from how they affect personal credit. Each of these factors affects business credit and personal credit differently.
Most personal accounts do not report late payments to your personal credit until they are 30 days or more past due. In contrast, business credit accounts report to business CRAs when an account is only one day late.
When someone checks your personal credit, there is a negative impact on your credit score. Hence, your personal credit score can go down. When a business loan provider checks your business credit score, there is no negative impact.
Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act, your consumer report can only be requested by those with “permissible purpose.” A permissible purpose may include the preparation of subpoenas or court orders, written instructions from the consumer, employment purposes with written authorization from a consumer, insurance underwriting purposes, credit transactions with a consumer, tenant screening, and national security investigations.
However, anyone can check your business credit score. The FCRA does not apply to business credit reports.
Your personal credit report has the name of the company holding each account reporting. Your business credit only lists the industry of the reporting account, not the company’s name.
Though it varies, most information stays on your personal credit for the life of the report. The average life of information on your corporate credit report is 3 years. Of course, averages can encompass a wide range.
Exact amounts are shown on your personal credit, but business credit reports show rounded amounts.
With personal credit, everyone reports your accounts and payments, or lack thereof, to the CRAs. Only about 7% of those who check business credit actually report accounts to the business credit CRAs.
The amount of debt you have in relation to the amount of credit available to you (credit utilization) makes a real impact on your personal credit score. If your cards are nearly maxed out, your score goes down. But with business credit, it doesn’t make any difference.
There is much less regulation when it comes to business credit. And there is virtually no regulation when it comes to correcting mistakes on your business credit.
You can get a free copy of your consumer credit report each year. In addition, there are a number of free credit monitoring services that let you get a peek at your credit score. These are typically updated at least once a month.
There is really no way to see your company credit report for free. Instead, you’ll need to use business credit monitoring services. They are not free, but if you choose the right one the benefit is well worth the cost.
At Credit Suite you can Monitor your Business credit scores and reports with D&B, Experian, and Equifax for only $24/ month. Considering that the business credit advantage plan from Experian is nearly $200 per year all by itself, this is a great deal. Here’s how to get it.
How Do I Check My Business Credit Scores?
It is important to know what is happening with your credit. Make certain it is being reported and take care of any mistakes ASAP. Get in the habit of taking a look at credit reports and digging into the specifics, not just the scores.
Currently, at D&B you can monitor here. At Experian, you can monitor your account here. And at Equifax, you can monitor your account here.
In late 2022, D&B monitoring prices range from $15 to $39 per month. Experian monitoring products range from $39.95 to $1,995 currently. Prices can change at any time, so check directly with the credit reporting agencies for current pricing.
Credit Suite clients can you can track their Business credit scores and reports with D&B, Experian, and Equifax as part of Bureau Insights tool. Find out more now. NAV no longer provides D&B data.
Update Your Record With the Credit Reporting Agencies
Update the information if there are errors or the relevant information is incomplete. At D&B, here’s where you can do so. For Experian, you can make corrections here. Find out what Equifax says about updating company information.
Business Credit Monitoring with Credit Suite
We can help you monitor business credit at Experian and D&B for considerably less than it would cost you at the CRAs. See: www.creditsuite.com/monitoring.
Disputes
Errors in your credit report(s) can be fixed. But the CRAs normally want you to dispute in a particular way.
Here are the direct links to accessing your credit reports from each CRA:
Here are the direct dispute links for your personal or company’s reports on each CRA:
FAQs
We look at your business Fundability(TM) before you apply for any accounts, then we help fix issues, establish a Business Credit Profile and then map a path to the best loans and credit lines for your business.
You can establish business credit without a personal guarantee or personal credit check making it easy to run your business without using your personal finances or harming your personal credit.
Our advisors and team are real people that love helping business owners like you.
Your success is our success.
When someone checks your personal credit, there is a negative impact on your credit score. When a lending institution checks your business credit score, there is generally no negative impact.
Y
Yes! Late payments will negatively impact your business credit score. Fortunately, timely payments of your bills is one of the easiest ways to turn around a low business credit score.
Most personal accounts do not report late payments to your personal credit until they are 30 days or more past due. Business credit accounts report to business CRAs when an account is only one day late.
Disputing credit report inaccuracies generally means you mail a paper letter with duplicates of any evidence of payment with it. These are documents like receipts and canceled checks. Never send the originals. Always send copies and retain the original copies.
The CRAs are getting better at accepting disputes online, so be sure to check.
Fixing credit report inaccuracies also means you specifically detail any charges you dispute. Make your dispute letter as clear as possible. Be specific about the problems with your report. If disputing by mail, be sure to use certified mail so that you will have proof that you mailed in your dispute.
D&B uses their Data Cloud, which includes data from a number of sources. These sources are also where other business credit CRAs gather their data from. These sources include LexisNexis, The Small Business Finance Exchange, public records, and company reported data.
The length of time information stays on your business reports averages three years. Sometimes it is seven years, sometimes a year, with a wide range in between. Often, information comes off after a certain amount of time.
Per Experian, bankruptcies stay for 7 to 10 years. It depends on the type of bankruptcy. Chapter 13 bankruptcy rolls off your credit report seven years from the filing date, while Chapter 7 bankruptcy stays for 10 years from the filing date.
You do not have to contact a credit agency, it happens automatically. Just check your report to be sure.
LexisNexis is a provider of legal, government, business and high-tech information sources. This data is used to help lenders, credit providers, and others to better understand the risks of loaning money or extending credit so lenders and credit providers can make better decisions. This helps credit providers and lenders spot fraud and avoid collections issues. A typical LexisNexis report on just one individual can run over 100 pages long.
Check out this video on how LexisNexis works.
LexisNexis uses innovative, proprietary technology. It is to help their customers prevent and get rid of fraud. They help increase efficiency by presenting information in a way that is easier for the average company owner to understand.
Over the span of their 40 years they have grown substantially. Today they have customers in over 100 countries and across multiple industries.
The SBFE is a not-for-profit entity that gathers data on small businesses from its members. The data is then used to compile comprehensive credit information. Lenders use this information to make credit decisions.
The Small Business Finance Exchange does not lend money. It also does not create or distribute credit reports. Certified vendors like D&B, Experian, and Equifax distribute the data they receive from the SBFE by creating credit analysis products using the information that the Small Business Finance Exchange provides.
CRAs then report the data to members who request a credit report on a business that is included.
Check out this video on how the SBFE works.