Tax is part and parcel of today’s society. It applies to businesses of all sizes, not to mention startups and small enterprises. In fact, you should be well informed about your tax responsibilities even before launching a business.

Image Source: https://unsplash.com/photos/person-holding-paper-near-pen-and-calculator-xoU52jUVUXA
However, keeping up with your tax commitment can be daunting. As a small business owner, you should understand the ins and outs of the tax laws and regulations. More importantly, stay on top of your tax obligations, whether federal, state, or local.
Now, what happens when you fail to comply with your tax responsibilities? You’ll face legal ramifications and financial losses for non-compliance. So, managing your taxes is imperative.
As such, discover ten effective tax management tips for your small business. But first things first, understand the impact of taxes on your business profits below.
Ready? Let’s dive right in!
The Impact of Taxes on Small Business Profits
Taxes are financial obligations every individual or business should pay to the government. Every small business owner knows these taxes generate income for the country. They fund various public programs and services to benefit the society and its people.
Now, you might be wondering what the tax obligations of small businesses are in the United States. Take a look at the table below:
| Types of Tax | Tax Descriptions and Examples |
| Income Taxes | These federal taxes apply to earnings from business ventures, employment, and investments in the U.S. Even state authorities impose their income taxes on top of the required federal taxes. |
| Employment Taxes | The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires U.S. businesses to file, report, and pay for various employment taxes. Employers are responsible for paying Social Security and Medicare taxes. They also withhold these from the workers’ wages as part of the employee benefits. |
| Self-employment Taxes | These taxes apply to individuals who work for themselves (or those operating sole proprietorships). Likewise, these include Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld from the employee’s paycheck. |
| Sales Taxes | These taxes get collected for the sales of goods or items. However, it varies from one state to another. Likewise, it depends on the nature of your business. Businesses are usually responsible for remitting taxes to the government. |
| Property Taxes | Same as homeowners, businesses with real estate ownership are subject to this type of tax. This tax depends on the property value as appraised by the local government. However, companies are responsible for paying for this regularly. |
| Excise Taxes | Some products or services may be subject to this tax type. Generally, businesses offering alcohol, tobacco, and gasoline disburse funds for excise taxes. However, those engaged in coal mining, oil and gas extraction, as well as sports betting are also paying for these taxes. |
| State Business Taxes | There are other taxes collected by your state other than those mentioned above. A few examples are franchise, gross receipts, and business privilege taxes. It’s best to consult your state authorities about the tax obligations for your small business. |
| Local Business Taxes | Some local authorities levy taxes on businesses operating within their jurisdictions. Examples are business licenses, occupational taxes, and utility taxes. Therefore, talk to your local authorities so that you won’t miss out on your tax responsibilities. |
Unfortunately, taxes comprise some of the biggest expenditures for startups and small businesses. They substantially affect their profitability and compromise their cash flow. That’s why some submit small business loan requirements to borrow money for settling tax obligations.
Unconvinced? Here are alarming statistics on small business taxes per NFIB:
- Three-fourths of small businesses are unincorporated pass-through entities. As such, they report business income on personal taxes.
- The tax compliance overheads are 67% higher for small businesses than for big companies. However, startups and small enterprises need to comply.
- Half of the small businesses encounter regular cash-flow problems. Federal, state, and local tax payments add up to such problems.
However, you don’t necessarily have to pay for all of these. You can be eligible for particular reliefs and allowances for tax avoidance or reduction. Further, it helps to set an accounting checklist and manage your taxes well.
How? Earn some tax management tips for your small business in the next section.
How To Manage Your Small Business Taxes Effectively
Effective tax management is crucial for your profitability and overall success. It helps you stay legally compliant, reduce tax liabilities, and avoid hefty penalties. That’s why companies and organizations are investing in tax management systems.
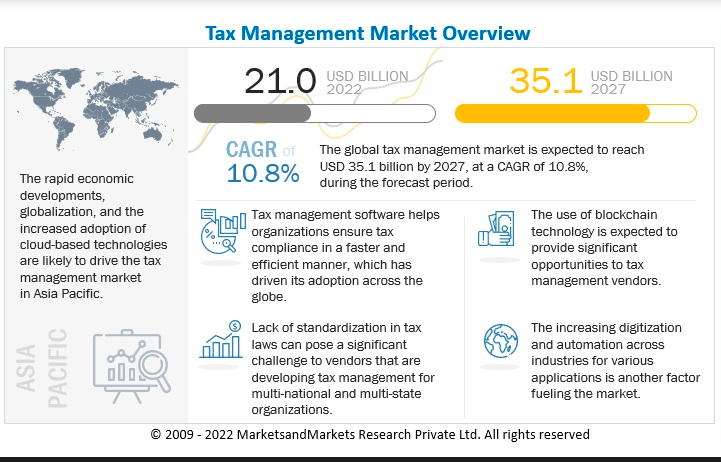
Image Source: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/tax-management-market-230446693.html
In fact, the global tax management market is projected to grow from $21 billion in 2022 to $35.1 billion by 2027. It’s forecasted to expand at a 10.8% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). Such market growth is due to the following factors:
- Increased financial transactions
- Changing tax legislative landscape
- Maintaining compliance with real-time reporting
- Mitigating financial risks
- High-quality tax data within systems
Tax management applies to startups and small businesses. However, it can be overwhelmingly complex if you lack experience in financial recording, tax reporting, and tax filing.
Fret not, as we’ll help you manage your small business taxes effectively. Here’s how:
1. Keep Accurate Tax Records
The first tax management tip is to have an accurate, complete, and up-to-date recording of all your financial transactions. You can achieve this through proper bookkeeping and accounting. While bookkeeping involves financial recording, accounting entails financial analysis, business reporting, and decision-making.
Jack Underwood, CEO and co-founder at Circuit, recommends tracking and recording income and expenses. “Understand that both impact your business taxes. Keep all receipts and invoices to make your tax reporting and filing more accurate, efficient, and seamless. That can help you stay fully compliant with your tax obligations.”
2. Plan for the Tax Season
It’s crucial to come prepared and ready for the tax season. It’s best to check with the IRS when you must file, report, and pay your taxes. Note that the IRS offers three options for tax years, as follows:
- Calendar Year: This calendar-based accounting period covers twelve months. It starts on January 1st and ends on December 31st.
- Fiscal Year: This accounting period also covers the twelve months. However, it doesn’t have to be the same as the calendar year. For instance, if your tax collection begins on April 1st, it ends on April 1st of the following year.
- Short Tax Year: This accounting period can be less than twelve months. It usually happens when your startup begins midyear or makes changes from the calendar to the fiscal year.
Early planning should be a part of your tax management strategy. It’s best to set aside time to review your financial statements every quarter. Calculate tax liabilities, pay estimated taxes, and prepare the required documents. Make necessary adjustments to ensure you’re on track for tax season.
3. Separate Business and Personal Finances
It’s easy to see small business owners mix up their personal money and business finances. They probably don’t have separate bank accounts for both.
Unfortunately, this move can be a recipe for financial chaos and business disaster. As a sole proprietor, you should have a business bank account. This approach can help with your proper tax management as well.
Eric Mills, Owner of Lightning Card Collection, recommends separating business and personal finances. “This makes it easier for you to track and manage your income and expenses. Also, this makes you more efficient in preparing and filing your taxes come the tax season.”
4. Classify your Business Type Correctly
Correct business classification is vital for your tax management. As you can see, business structures can impact tax obligations. Consider the following structures:
- Sole proprietorships (Single Member LLC or Sole Proprietor)
- Businesses partnerships (Limited Liability Partnership and Limited Liability Company)
- Corporations (C Corporation and S Corporation)
Know that they all have different tax requirements and liabilities. As such, consult with a tax professional to determine the appropriate structure for your small business. Then, ensure that you’re complying with all necessary tax requirements.
5. Manage Your Payroll Effectively
Small businesses employing staff are responsible for withholding and remitting employment taxes. As mentioned, you make income tax and insurance contributions for your employees. The last thing you want is to get small business funding just to be able to cover all your payroll obligations.
You should ensure accurate tax reporting and disbursements. Consider hiring or outsourcing payroll functions for your small business. While at it, ensure that your payroll officers have the experience and expertise in tax management.
6. Capitalize on Tax Deductible
Did you know that tax deductibles exist? As a small business owner, capitalize on all tax-deductible expenditures to decrease tax liabilities. For example, you can reduce expenses for business travel, office supplies, and equipment.
Start by checking the tax deductions for small businesses, which include the following:
- Rent
- Home office
- Advertising
- Vehicle
- Travel
- Employee salaries
That said, see what you can take advantage of. Check your eligibility and tax requirements to avail yourself of these deductibles. Consult with a tax professional to help you make informed decisions.
7. Stay Abreast of Tax Laws and Regulations
You must understand the laws and regulations by heart to know your tax obligations. As they are ever-changing, you should always stay up-to-date with some changes. More importantly, ensure you are always compliant with these laws and regulations.
Javier Muniz, CTO at LLC Attorney, suggests working with legal officers. “These professionals know the ins and outs of the tax laws and regulations. They can help you navigate through complex legal requirements. They’ll help ensure 100% adherence and avoid fines, penalties, and legal issues.”
8. Select the Right Accounting Method
Earlier, we defined accounting not only as a financial recording. The process also involves financial analysis, business reporting, and decision-making. It’s a vital part of your tax management strategy.
That said, select the best accounting method that can impact your tax reporting and filing. Below are some to consider:
- Cash accounting involves recording financial transactions as you receive cash or when your customers pay you. It’s a straightforward method used by small businesses, which will help simplify your tax management process.
- Accrual accounting entails recording financial transactions as they happen, whether you receive the payment or not. Big companies employ this method, often required for some tax purposes.
- Hybrid accounting is a combination of both cash and accrual accounting. It records financial transactions on a cash basis and others on an accrual basis. More often than not, this method is best for businesses of all sizes.
Overall, choosing an accounting method can impact your tax liabilities. So, pick the one best suited for your business size, needs, and budget.
9. Hire a Tax Professional
Aside from working with a legal consultant, hire a tax professional for your small business. As an entrepreneur, you must focus on making money and growing your business. Unfortunately, dealing with taxes can be tedious and cumbersome.
As such, it’s better to entrust your non-core functions like tax reporting and filing to a reliable tax specialist. Sure, you may add one to your payroll. However, this professional can help you stay tax-compliant, reduce your tax liabilities, and avoid penalties. That will help you save money long-term!
10. Take Advantage of Software Automation
The use of software automation has become all the rage these days. It applies to tax management as well. In fact, the global tax management software market could grow from $18.74 billion in 2022 to $39.71 billion by 2030 at a 10.1% CAGR.
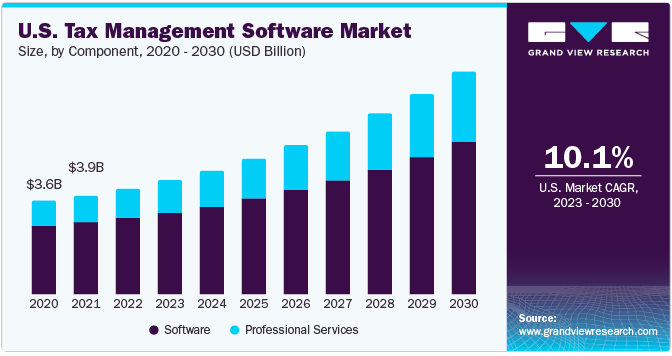
Image Source: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/tax-management-software-market-report
Corey Donovan, President of Alta Technologies, recommends investing in technology for tax accounting. “In this time and age, companies of all sizes should harness the power of technology. Small businesses should consider leveraging software automation to accelerate their processes. That said, invest in accounting software for tax accountants.”
Software automation helps you perform the following:
- Automatically record financial transactions;
- Maintain and update accurate financial records;
- Manage tax information;
- Perform tax computation; and
- Automate tax reporting and filing;
With this in place, you can streamline your tax management processes for your small business. That will help you save time, money, and effort in preparing and filing your taxes.
Staying on Top of Your Small Business Taxes
Tax management is integral to your business operation. As a small business owner, you must stay on top of your tax commitment to ensure regulatory compliance, reduce expenditures, and increase profits.
That said, consider the ten tax management tips recommended above. By implementing these, you can take control of your tax obligations. That will, ultimately, minimize your risks and maximize your revenues for business growth and success!


